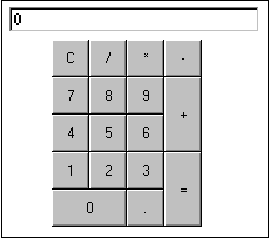
Figure 2: A Calculator.


Now, let us consider how to build the calculator depicted in Figure 2. The calculator is composed of a display and a board with many buttons. The display is simply a text field which is already available as a base class. Therefore, we only need to get the Board class ready to build a calculator.

Figure 2: A Calculator.
The following shows the class for building the board:
Class Board {
component Button b[9]; // Buttons "0",...,"9"
component Button bc {text == "C"};
... // Buttons "+","-","*","/",".","="
for (i in 0..9) b[i].text == String(i);
grid({{bc,bdiv,bmul,bsub},
{b[7],b[8], b[9], badd},
{b[4],b[5], b[6], badd},
{b[1],b[2], b[3], beq },
{b[0],b[0], bpoint,beq}});
}
The for statement constrains the values for the text attributes
of the digit buttons. The grid constraint constrains the
positions for the buttons. Notice that a component may spread over
several grids.
We are now ready to build the calculator. Besides the layout of the display and the board, we must also specify the actions that must be taken when buttons are clicked.