Examples
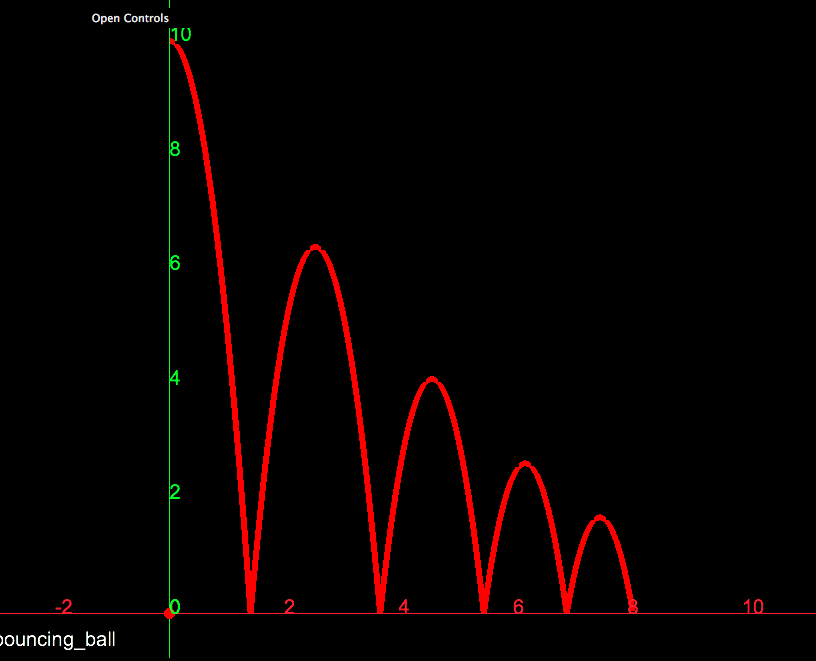
Bouncing particle †
// y stands for the height of the ball
INIT <=> y = 10 & y' = 0. // initial state
FALL <=> [](y'' = -10). // falling
BOUNCE <=> [](y- = 0 => y' = -4/5*y'-).
// if the ball reaches the ground, it bounces
INIT, FALL << BOUNCE. // FALL is weaker than BOUNCE
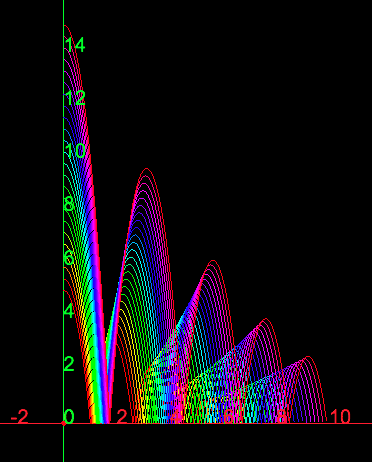
Bouncing particle with a parametric initial height †
INIT <=> 5 < y < 15 & y' = 0. // the initial height is uncertain FALL <=> [](y'' = -10). BOUNCE <=> [](y- = 0 => y' = -4/5 * y'-). INIT, FALL << BOUNCE.
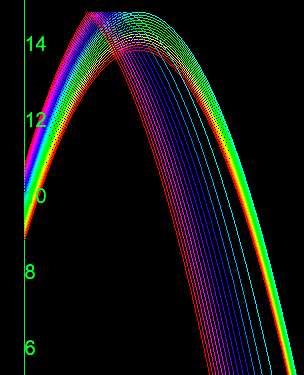
Bouncing particle in a parabolic vase †
/**
* bouncing particle on a curve of f(x) = (1/2) * x^2
*/
INIT <=> x = 1/2 & y = 10 & x' = 0 & y' = 0 & [](k = 1).
A <=> [](x'' = 0 & y'' = -98/10).
/**
* sin = f'(x) / (1+f'(x))^(1/2)
* cos = 1 / (1+f'(x))^(1/2)
* new x' = (-k * sin^2 + cos^2) * x' + (k+1) * sin * cos * y'
* new y' = (k+1) * sin * cos * x' + (sin^2 + (-k) * cos^2) * y'
*/
SC <=> [](s = (x-)/(1+(x-)^2)^(1/2)
& c = 1 /(1+(x-)^2)^(1/2)).
BOUNCE <=> [](y- = (1/2) * (x-)^2 =>
x' = ( (-k) * s^2 + c^2 ) * x'- + ( (k+1) * s * c ) * y'-
& y' = ( (k+1) * s * c ) * x'- + ( s^2 + (-k) * c^2 ) * y'- ).
INIT, SC, A << BOUNCE.
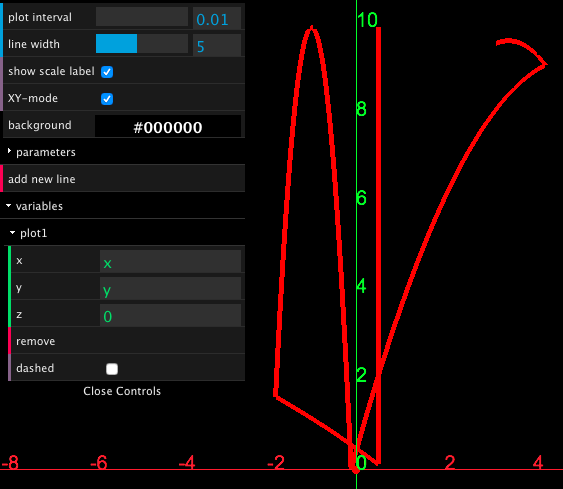
Bouncing particle in a circle †
INIT <=> x = 0 /\ 0.5 < y < 0.6 /\ x' = 2 /\ y' = 1.
// the initial position is uncertain
RUN <=> [](x'' = 0 /\ y'' = 0).
BOUNCE <=> []((x-)^2 + (y-)^2 = 1 =>
x' = x'- - (x- * x'- + y- * y'-) * 2 * (x-)
/\ y' = y'- - (x- * x'- + y- * y'-) * 2 * (y-)
).
INIT, RUN<<BOUNCE.
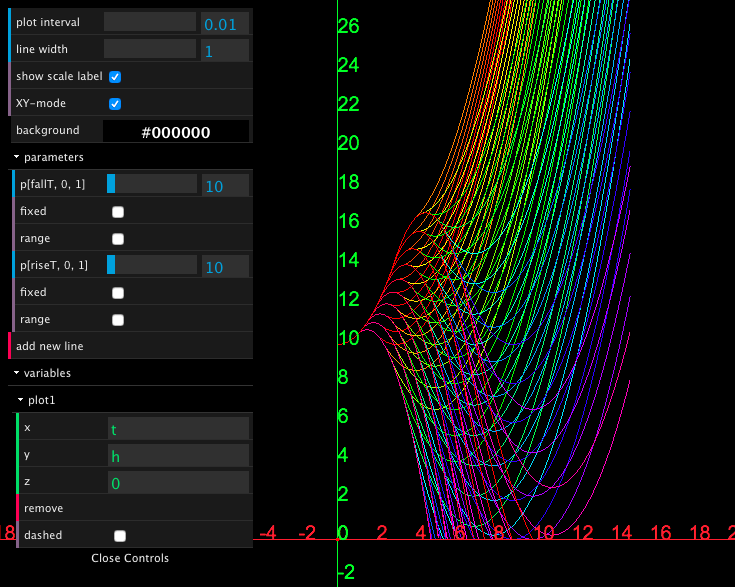
Hot-Air Balloon with multiple parameters †
/* A program for a hot-air balloon that repeats rising and falling */
// The initial condition of the balloon and the timer
// h: height of the balloon
// timer: timer variable to repeat rising and falling
INIT <=> h = 10 /\ h' = 0 /\ timer = 0.
// parameters
// duration: duration of falling
// riseT: duration of rising
PARAM<=> 1 < fallT < 4 /\ 1 < riseT < 3
/\ [](riseT' = 0 /\ fallT' = 0).
// increasing of timer
TIMER <=> [](timer' = 1).
// rising of the balloon
RISE <=> [](timer- < riseT =>h'' = 1).
// falling of the balloon
FALL <=> [](timer- >= riseT => h'' = -2).
// reset the timer to repeat rising and falling
RESET <=> [](timer- >= riseT + fallT => timer=0).
// assertion for bounded model checking
ASSERT(h > 0).
// constraint hierarchies
INIT, PARAM, FALL, RISE, TIMER<<RESET.
Bouncing particle with magnetic force †
INIT <=> y=10 & y'=0 & mag=0 & timer=0.
FALL <=> [](y''=-10+mag).
BOUNCE <=> [](y-=0=>y'=-y'-).
TRUE <=> [](1=1).
TIMER <=> [](mag'=0&timer'=1).
SWITCHON <=> [](timer-=1=>mag=12&timer=0).
// The magnetic force may be switched on at every one second
SWITCHOFF <=> [](timer-=1=>mag=0&timer=0).
// The magnetic force may be switched off at every one second
INIT,TIMER<<(SWITCHOFF,SWITCHON)<<TRUE,FALL<<BOUNCE.
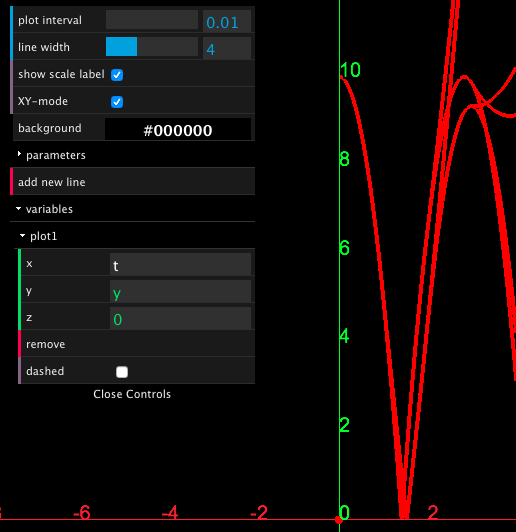
Bouncing particle thrown toward a ceiling †
INIT <=> 9 < y < 11 & y' = 10. FALL <=> [](y'' = -10). BOUNCE <=> [](y- = 15 => y' = -(4/5)*y'-). INIT, FALL << BOUNCE.
- In this program, the trajectories change qualitatively dependent on the initial height \( y_0 \).
- If \( 9 < y_0 < 10 \), the ball doesn't reach the ceiling.
- If \( y_0 = 10 \), the ball touches the ceiling, but the velocity remains continuous.
- If \( 10 < y_0 < 11 \), the ball bounces on the ceiling.
- If \( 9 < y_0 < 10 \), the ball doesn't reach the ceiling.
- HyLaGI performs such a case analysis automatically.
Last-modified: 2017-03-17 (Fri) 08:42:45 (3045d)