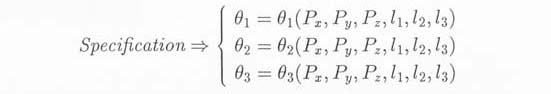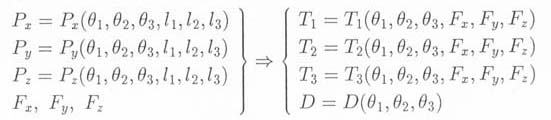- Analyze and evaluate the robot by
- Solving Inverse Kinematics,
- Calculating the Torque working on each Joint, and
- Calculating the Manipulability of Robot being designed.
Demonstration
The handling robot in the following "handling robot design support system"
demonstrations is a robot with 3 joints and 3 arms.
1) Forward Kinematics
Deducing the position of the end-effector (Px,Py,Pz) in terms of
the length of each arm (l1,l2,l3) and the rotation angle of each joint
(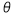 1,
1,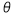 2,
2,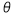 3).
2) Inverse Kinematics
Calculating the desired joint rotation angles (
3).
2) Inverse Kinematics
Calculating the desired joint rotation angles (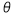 1,
1,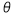 2,
2,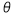 3) to move the
end-effector to a given position (Px,Py,Pz). Since this problem
have more than two solutions, filtering to reduce the number of
solutions is demonstrated by restricting the rotation angle of a
certain joint.
3) Calculation of Torque and Evaluation of Manipulability
By using the forward kinematics results (Px,Py,Pz) and giving the
force working on the end effector (Fx,Fy,Fz), equations to calcu-
late the torque working on each joint (T1,T2,T3) and the manipu-
lability (D) are deduced. Then, by placing constraints on moving
the end-effector, the equations for torques and manipulability are
simplified.
- 105 -
3) to move the
end-effector to a given position (Px,Py,Pz). Since this problem
have more than two solutions, filtering to reduce the number of
solutions is demonstrated by restricting the rotation angle of a
certain joint.
3) Calculation of Torque and Evaluation of Manipulability
By using the forward kinematics results (Px,Py,Pz) and giving the
force working on the end effector (Fx,Fy,Fz), equations to calcu-
late the torque working on each joint (T1,T2,T3) and the manipu-
lability (D) are deduced. Then, by placing constraints on moving
the end-effector, the equations for torques and manipulability are
simplified.
- 105 -
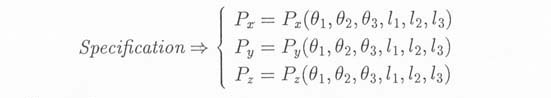
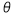 1,
1,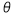 2,
2,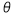 3).
3).
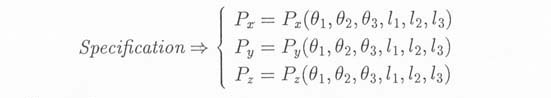
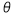 1,
1,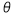 2,
2,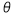 3) to move the
end-effector to a given position (Px,Py,Pz). Since this problem
have more than two solutions, filtering to reduce the number of
solutions is demonstrated by restricting the rotation angle of a
certain joint.
3) to move the
end-effector to a given position (Px,Py,Pz). Since this problem
have more than two solutions, filtering to reduce the number of
solutions is demonstrated by restricting the rotation angle of a
certain joint.