ABSTRACT
Quixote system provides important facilities required for knowledge infor-
mation processing, such as knowledge representation and inferences. Quixote
also provides basic functions for constructing an integrated knowledge-base
management system on top of Kappa-P, a nested relational DBMS.
KEY FEATURES
Quixote is a language for deductive object-oriented databases (DOODs),
and can be seen as an extended logic programming language with its object-
orientation features, subsumption constraints, and hierarchical modules.
Object Identity: Using extended terms (object terms), representing in-
trinsic properties of objects, as object identifiers
Subsumption Constraint: Using subsumption relations among object
terms as constraints for properties
Property Inheritance: Using subsumption relations for property inher-
itance among objects including exceptions and multiple inheritance
Module: Introducing the modules having object terms as their identifiers
in order to modularize knowledge bases, and the inter-module (submod-
ule) relation for defining hierarchical structure of knowledge bases
Rule Inheritance: Importing and exporting rules among modules by sub-
module relations and set-theoretical operations including exception spec-
ified by modes of rules
Conditional Query: Introducing queries having additional assertions to
a knowledge base, and answers with assumed constraints on properties
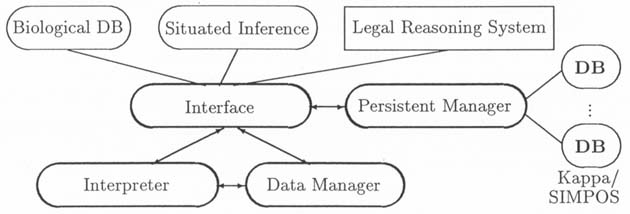
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
 |
- 81 -

